Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Varnished wire, a critical component in electrical engineering, plays a pivotal role in enhancing insulation and improving the efficiency of electrical devices and machinery. The global varnished wire market is projected to witness a robust growth rate, with an expected value of USD 3.1 billion by 2025, according to recent market analysis from Industry Research Firm. This exponential increase can be attributed to the rising demand for energy-efficient and high-performance electrical systems across various industries, including automotive, consumer electronics, and renewable energy.
Experts like Dr. Emily Carter, a leading authority in electrical materials, emphasize the significance of varnished wire in modern applications. She states, "The use of varnished wire not only ensures the longevity of electrical components but also optimizes their performance under varying environmental conditions." This underscores the importance of varnished wire in mitigating electrical failures and enhancing the overall reliability of electrical systems. As industries continue to evolve and innovate, the role of varnished wire is expected to expand, offering new opportunities for development and application in next-generation electrical engineering solutions.
Varnished wire is an insulated conductor widely used in electrical engineering, characterized by its coating of insulating varnish that enhances its properties and applications. The most common form of varnished wire is enameled wire, which is produced by applying a thin layer of insulation to a copper or aluminum wire. This insulation serves as a protective barrier, preventing short circuits and electrical leakage, while also providing resistance against environmental factors such as moisture and heat. According to industry reports, the global demand for varnished wires is projected to grow by approximately 7% annually, reflecting their importance in modern electrical applications.
The characteristics of varnished wire include high thermal resistance, flexibility, and excellent electrical insulation properties. The varnish used typically allows the wire to operate at high temperatures, often exceeding 180°C, making it ideal for applications in motors, transformers, and inductors. Additionally, varnished wire is lighter and more compact than traditional insulated wires, which contributes to its efficiency in space-constrained designs. Furthermore, recent advancements in varnish technology have led to the development of coatings that enhance the wire's chemical resistance and mechanical strength, thereby broadening its applicability in harsh industrial environments. As the electrical engineering sector continues to evolve, varnished wire remains a crucial component in the achievement of more efficient and reliable electrical systems.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | Varnished wire is insulated wire coated with varnish to enhance electrical insulation and mechanical protection. |
| Material Composition | Typically made from copper or aluminum with a layer of varnish for insulation. |
| Key Characteristics | High thermal resistance, excellent dielectric properties, and good mechanical strength. |
| Applications | Used in transformers, motors, generators, and various electrical appliances. |
| Temperature Rating | Varnished wires typically have temperature ratings ranging from 130°C to 220°C. |
| Benefits | Improved durability, resistance to moisture, and enhanced electrical performance. |
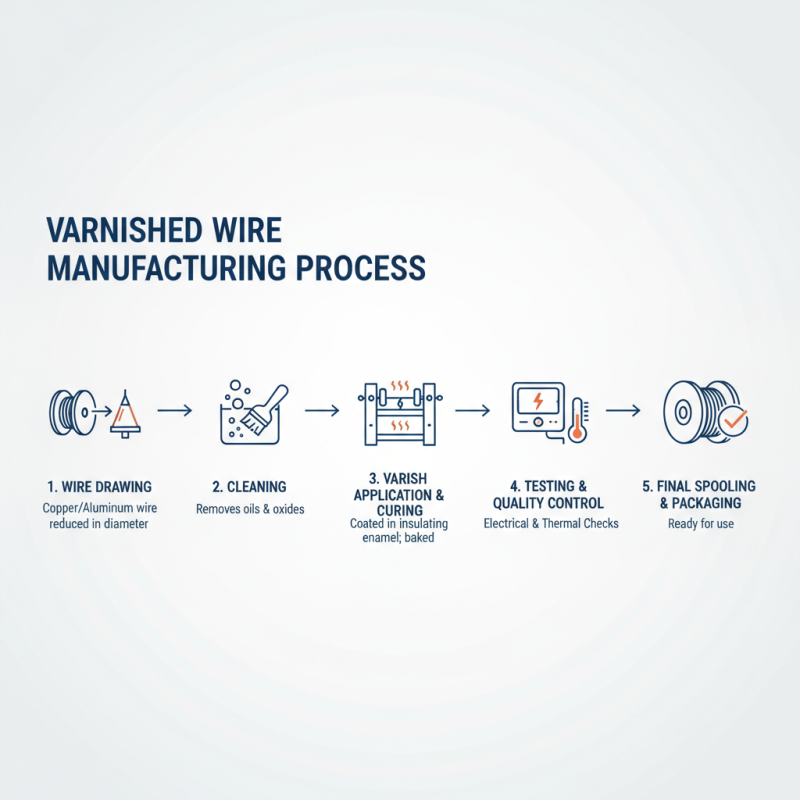
The manufacturing process of varnished wire involves several critical steps that ensure the final product possesses the desired electrical and thermal properties. Initially, copper or aluminum wire is drawn to the required gauge. This is done by passing the metal through a series of dies that gradually reduce its diameter while increasing its length. Once the wire is formed, it undergoes a cleaning process to remove any contaminants such as oils or oxides that may interfere with the adhesion of the varnish.
Following the cleaning, the wire is coated with a varnish, typically an insulating resin that provides both electrical insulation and mechanical protection. The application of the varnish can be performed using various techniques, including dip coating, spray coating, or extrusion. Each method has its advantages, depending on the desired thickness of the insulation and production efficiency. After coating, the wire is usually subjected to a curing process, which typically involves heating to enable the varnish to harden and bond effectively to the wire surface. This curing step is crucial, as it determines the durability and performance of the varnished wire in its final applications.
The resultant varnished wire is now ready for various electrical engineering applications, such as in motor windings, transformers, and coils, where its insulating properties and flexibility are essential for functionality and reliability. The manufacturing process not only enhances the wire's performance but also extends its lifespan, making it a vital element in modern electrical systems.
Varnished wire, often referred to as enameled wire, is a type of insulated copper or aluminum wire coated with a layer of varnish, which provides electrical insulation while maintaining efficient conductivity. This unique combination of properties makes varnished wire highly suitable for various applications in electrical engineering. Its use can be found across multiple domains, notably in the manufacturing of electric motors, transformers, and generators, where reliable performance and insulation are critical.
In electric motors, varnished wire is utilized in winding coils, where it helps in reducing the risk of short circuits while allowing heat dissipation during operation. Additionally, in transformers, the high insulation resistance and thermal endurance of varnished wire ensure that electrical energy is efficiently transferred with minimal losses. Furthermore, in the field of telecommunications, varnished wire is commonly used in inductors and relays, where its lightweight and compact nature contribute to the overall efficiency and performance of electronic circuits. As the demand for high-performance electrical components continues to grow, the significance of varnished wire in achieving these specifications becomes increasingly paramount.

Varnished wire, commonly utilized in electrical engineering, offers significant benefits that enhance the efficacy and longevity of electrical devices. One of the primary advantages is its excellent insulation properties. The varnish coating provides a robust dielectric barrier that prevents short circuits and electrical leakage, thereby ensuring reliability and safety in various applications. This feature is particularly essential in high-voltage environments where insulation integrity is critical to performance and safety standards.
Additionally, varnished wire enhances the thermal stability of electrical devices. The varnish not only protects the wire from moisture and environmental factors but also improves its ability to withstand high temperatures. This thermal resilience reduces the risk of overheating and extends the operational lifespan of electrical components. Furthermore, the smooth surface of varnished wire facilitates easy winding in motors and transformers, contributing to more efficient energy transfer and reduced electrical losses. Overall, the use of varnished wire is instrumental in optimizing the performance and durability of electrical devices across various sectors.
When evaluating wire insulation options in electrical engineering, varnished wire stands out due to its unique properties. Varnished wire is typically coated with a layer of insulating varnish, which enhances its electrical performance and mechanical durability. This insulation method is particularly valued for its ability to withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for applications where heat dissipation is crucial, such as in transformers and motor windings.
In comparison to other types of wire insulation, such as PVC or rubber coatings, varnished wire offers a higher temperature tolerance and improved resistance to chemical solvents. While PVC insulation may be more flexible and cost-effective, it typically struggles in high-temperature environments and can degrade over time when exposed to certain chemicals. Rubber, while also flexible and providing good insulation, may not match the thermal stability levels of varnished wire. Thus, for applications demanding high performance under extreme conditions, varnished wire often becomes the preferred choice among engineers looking for reliability and longevity in electrical components.
This chart illustrates the insulation resistance and thermal stability of various types of wire insulation used in electrical engineering, highlighting Varnished Wire's advantageous properties in comparison to others.