Leave Your Message
-
Phone
-
E-mail
-
Whatsapp
Enameled Magnet Wire is a crucial component in the field of electrical engineering, playing a significant role in the manufacturing of various electrical devices. According to Dr. James Harris, an expert in the electrical materials industry, "Enameled Magnet Wire serves as the backbone of numerous applications, ensuring both efficiency and durability in electrical systems." This specialized wire consists of a copper or aluminum core coated with a thin layer of insulation, allowing for reliable electrical conductivity while minimizing energy loss.
The applications of Enameled Magnet Wire span a wide range of industries, from motors and transformers to renewable energy systems. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist moisture makes it an ideal choice for equipment that requires high performance under demanding conditions. As the demand for energy-efficient solutions grows, the significance of Enameled Magnet Wire continues to rise, paving the way for innovations in electrical engineering and technology. Understanding its properties and applications is essential for engineers and designers aiming to develop advanced electrical devices that meet today’s technological demands.

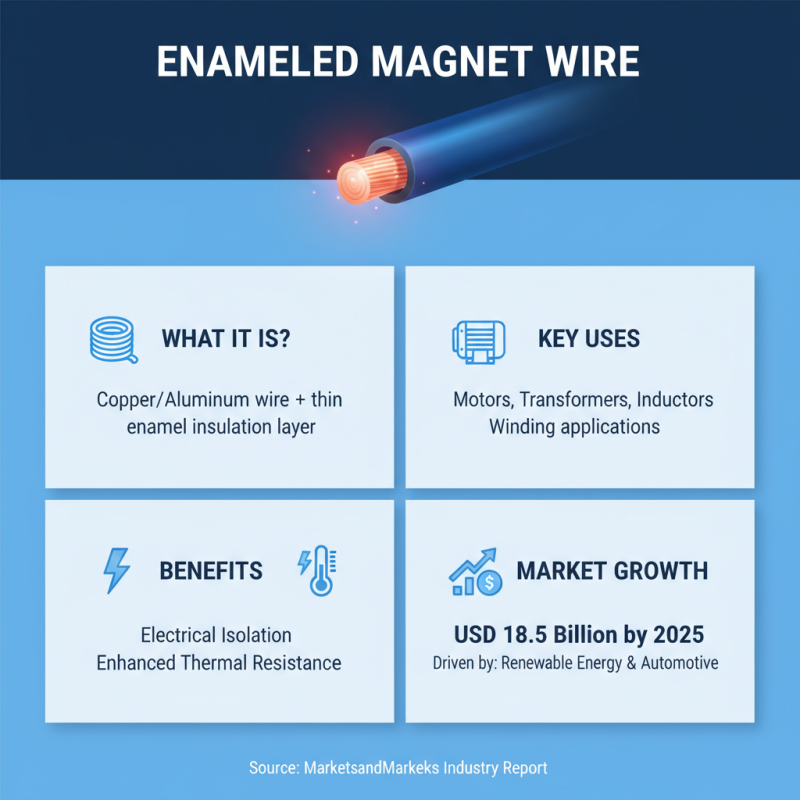
Enameled magnet wire, also known as magnet wire, is a type of copper or aluminum wire that is coated with a thin layer of insulation, typically made from enamel. This unique coating allows the wire to be used in various electrical applications, particularly in the winding of motors, transformers, and inductors. The enamel insulation not only provides electrical isolation but also enhances the wire's thermal resistance, enabling it to withstand higher temperatures. According to a recent industry report by MarketsandMarkets, the enameled magnet wire market is projected to reach USD 18.5 billion by 2025, driven by its growing applications in renewable energy systems and the automotive sector.
The composition of enameled magnet wire plays a critical role in its performance. The wire usually comprises a copper core, which is favored for its excellent conductivity, surrounded by an insulating layer made from thermoset or thermoplastic enamel materials. These enameled coatings come in varying thicknesses and dielectric strengths, tailored to meet specific application requirements. Industry insights indicate that the choice of insulation can significantly affect the wire's efficiency and longevity. For example, a study by Freedonia Group highlights that wires with higher thermal ratings can operate effectively in environments exceeding 200 degrees Celsius, vital for applications in electric vehicles and high-performance electrical equipment.
Enameled magnet wire is a vital component in electrical engineering, particularly in the manufacturing of motors, transformers, and inductors. The manufacturing process of enameled magnet wire begins with the selection of high-quality copper or aluminum wire. These materials are preferred due to their excellent electrical conductivity. According to a report by Mordor Intelligence, the global magnet wire market is expected to grow at a CAGR of around 3.5% from 2021 to 2026, indicating a significant demand for this specialized wire in various applications.
Following the selection of the base wire, it undergoes a series of processes that include cleaning, enameling, and curing. The wire is first cleaned to remove any contaminants that might affect the bonding of the enamel. Subsequently, it is coated with multiple layers of insulating enamel through either a solvent-based or a non-solvent process. This not only enhances the wire’s dielectric properties but also provides protection against environmental factors. A recent study noted that the major types of insulation used in enameled wire include polyurethane and polyester, each offering distinct advantages depending on the specific application. The final step involves curing the enamel, which solidifies the insulation and ensures its durability and thermal stability, ultimately making enameled magnet wire an indispensable element in modern electrical engineering.
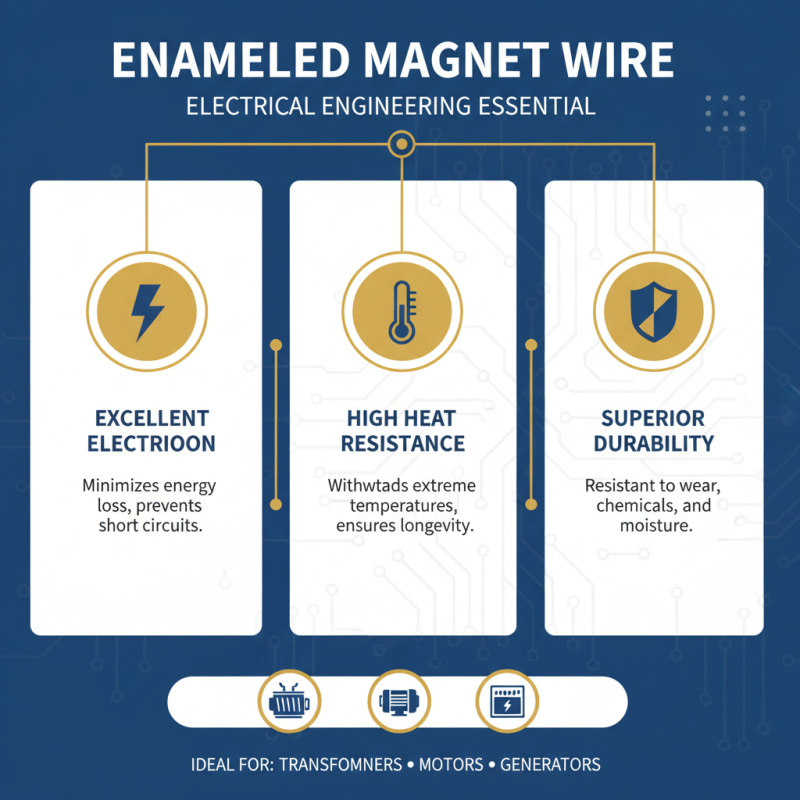
Enameled magnet wire, a subtype of magnet wire coated with an insulating layer of enamel, exhibits unique properties that make it indispensable in electrical engineering. The primary benefits of enameled magnet wire include its excellent electrical insulation, heat resistance, and durability. These characteristics enable it to efficiently conduct electricity while minimizing energy loss, making it ideal for applications such as transformers, motors, and generator windings.
Moreover, the global market for enameled wire is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6% over the next few years. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient electric motors and transformers in various industries. The chemical stability and resilience of enameled magnet wire also contribute to its longevity and reliability in high-stress environments, further solidifying its role in modern electrical applications. With continuous advancements in materials science, the development of new formulations for enameled wire is expected to enhance its performance and broaden its scope of application, ensuring its relevance in future electrical engineering innovations.
Enameled magnet wire is an essential component in various electrical engineering applications, particularly in the production of electric motors, transformers, and inductors. Its construction involves a copper or aluminum wire coated with a thin layer of insulation, which not only prevents short-circuiting but also enhances the wire's thermal and electrical conductivity. The global market for enameled magnet wire is projected to witness significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions in industrial and electronic sectors, anticipated to reach several billion USD by 2033.
In electrical engineering, enameled magnet wire finds its most common applications in the manufacturing of coils, solenoids, and electromagnetic devices. For example, in electric vehicle (EV) technology, magnet wire plays a critical role in the performance of charging systems and powertrains. Recent studies emphasize the importance of high-quality magnet wires, as their efficiency directly affects the overall energy consumption and operational lifespan of electrical systems. The innovation in materials, such as the introduction of advanced enamels that improve thermal resistance, is also seen as a pivotal factor for enhancing the reliability of electrical components in rapidly evolving industries like IoT and renewable energy systems.
| Application | Description | Wire Gauge | Insulation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Motors | Used in the winding of electric motors for electrical energy conversion. | AWG 18 - 26 | Polyester, Polyimide |
| Transformers | Serves as the winding material for electrical transformers enhancing voltage transformation. | AWG 12 - 30 | Enamel, Nylon |
| Inductors | Utilized in inductors to store energy in a magnetic field. | AWG 26 - 34 | Polyurethane, Enameled |
| Relays | Winding for electromagnets in relays for controlling circuit operation. | AWG 20 - 30 | Polyester, Epoxy |
| Speakers | Used in the voice coil of speakers for sound production. | AWG 22 - 30 | Polyurethane, Vinyl |
Enameled magnet wire is a crucial component in electrical engineering, known for its insulation and ability to conduct electricity efficiently. The coating provides a layer of protection, which not only prevents electrical shorts but also enhances the wire's durability in various applications such as transformers, motors, and coils. Compared to other types of magnet wire, like bare copper or aluminum wire, enameled magnet wire offers superior insulation properties and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-temperature environments.
When evaluating different types of magnet wire, the properties of glass-coated wires should also be considered. These wires present unique advantages, particularly their resistance to moisture and environmental factors. However, traditional enameled magnet wires typically excel in flexibility and ease of handling. Conductivity and magnetic performance are key factors in applications, leading to a comparative analysis that highlights the strengths of enameled wires in electrical devices.
**Tips:** When selecting magnet wire for your project, consider the operating environment and electrical requirements. If you're working in a high-heat situation, enameled magnet wire may be the better choice due to its thermal resistance. Additionally, always verify the wire's insulation rating to ensure it meets the necessary safety standards for your application.
This chart compares the electrical resistance of different types of magnet wire used in electrical engineering applications. Enameled magnet wire exhibits the lowest resistance, making it a popular choice in many scenarios due to its efficient conductivity.